


WHAT IS N.D.T. ? NDT technicians perform the necessary tests to locate the indicators and discontinuities that may cause failures shutting down systems. These tests are performed in a manner that does not affect the future usefulness of the object or material the name “nondestructive.” NDT allows for careful and thorough material evaluation without the need for deconstruction or damage. NDT can be used prior to the use of a component for the sake of quality control. NDT is also used to detect service conditions caused by wear, fatigue, corrosion, stress, or other factors which affect reliability.
Visual Examination can be an effective way to recognize surface defects that could affect components. Visual Examiners use the basics of how a part is manufactured, the function of the human eye, lighting requirements, and precise measuring tools to evaluate materials. Camera systems and aids such as borescopes may also be used to recognize and measure features of a component.
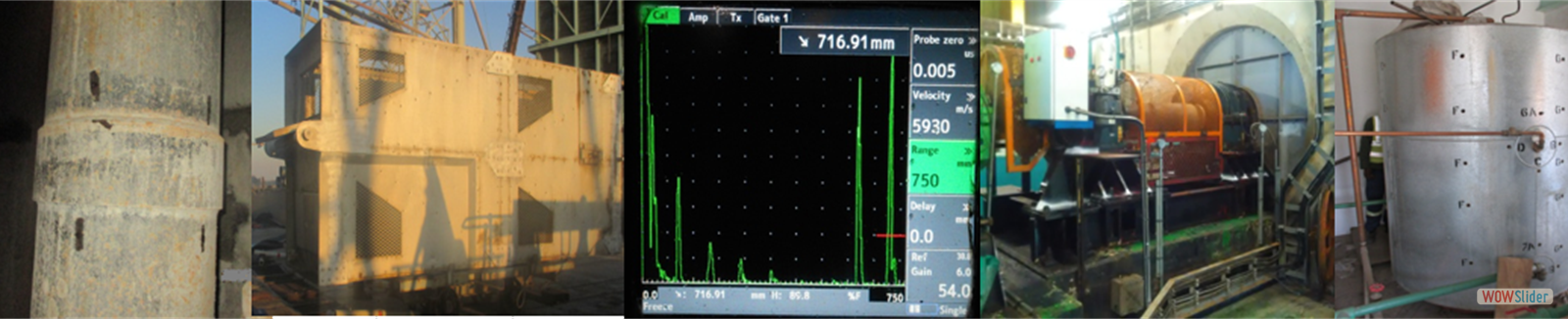
Ultrasonic Examination uses high-frequency sound waves which are transmitted into a material to detect discontinuities or locate changes in material characteristics. Sound is introduced into the object being examined and reflections from internal imperfections, areas of acoustic impedance, or varying geometrical surfaces are returned to a receiver.
Non-destructive measurement(gauging) of the local thickness of a solid element based on the time taken by the ultrasound wave to return to the surface. This type of measurement is typically performed with an ultrasonic thickness gauge. Thickness testing is used to monitor metal thickness or weld quality in industrial settings such as mining.
Magnetic Particle Examination is accomplished by inducing a magnetic field into a ferromagnetic material and applying iron particles to the surface of the item being examined. Surface and near-surface discontinuities affect the flow of the magnetic field within the part causing the applied particles to gather at locations of flux leakage, thus producing a visible indication of the irregularity on the surface of the material.
Penetrant Examination is performed with a dye solution. Once applied to the surface, the dye will effectively penetrate any surface-breaking cavity. Excess solution is removed from the object. A developer is then applied to draw out any penetrant that remains unseen. With fluorescent dyes, ultraviolet light is used to make the “bleed-out” fluoresce brightly, allowing imperfections to be readily seen. With visible dyes, a color contrast between the penetrant and developer makes the "bleed-out" easy to see.
Measuring the permanent depth of indentation produced by a force/load on an indenter. First, a preliminary test force is applied to a sample using a diamond or ball indenter. This preload breaks through the surface to reduce the effects of surface finish. After holding the preliminary test force for a specified dwell time, the baseline depth of indentation is measured. The Rockwell hardness test method, as defined in ASTM E-18, is the most commonly used hardness test method.
Recommended: sheave profiling is to determine the side wear and the depth wear of a sheave and gauges to examine the rope groove size.
Of all the factors which have some influence on the winding of a rope on a smooth drum, the fleet angle has the greatest effect. Fleet angle is usually defined as the included angle between two lines, one which extends from a fixed sheave to the flange of a drum and the other which extends from the same fixed sheave to the drum in a line perpendicular to the axis of the drum.
The purpose of spark testing is to determine if there are leaks in the rubber lining, and if so, their locations. It is not to test the conductivity of the rubber lining thus In testing one must be careful not to cause pinhole damage to the rubber. Rubber defects are marked to determine the damage to the linners